|
1. Introduction
The Deployment of QoS in the current networks is becoming an usual practice that network operators done in order to make
more efficient all the investment needed for the network deployment.
Furthermore, more and more common user applications make that the users demand a specific QoS which requires the sign of
a SLA with a network operators. The fulfilment in the signed agreements by both user and network operator is a must that
only can be checked with the proper equipment.
6QM IST project (http://www.6qm.org) deals with these topics
by developing a Measurement system, called OpenIMP, being able to measure different metrics in order to know the QoS provided in the
IPv6 network. The most important newness of these systems (programs and/or equipments) is that they are developed for working in IPv6
networks. This system is able to measure several parameters related to QoS in order to know the real QoS that user applications or
network operators have available in their networks.
The 6QM project has already developed a prototype of such system, which is pretty fully operational according to its
specifications. As part of 6QM task is the deployment and evaluation of its measurement prototype in large IPv6 networks.
As Euro6IX and 6NET are the main IST IPv6 research networks, they are a natural field where the 6QM prototypes can be deployed
and evaluated, which is supported by the fact that some Euro6IX and 6NET partners are 6QM partners also.
This document gives the necessary information in order to deploy in Euro6IX network the IPv6 QoS Measurement Probes developed by
IST 6QM project., according to the planned QoS activity roadmap for Y3.
2. 6QM PROTOTYPE DEPLOYMENT
2.1. OpenIMP prototype description
The OpenIMP prototype deals with the tasks needed to measure the QoS parameters of the traffic going to the IPv6 networks which
are measured. It is not only a typical passive measurement system but also it introduces new concepts on the measurement field. Some
of the more relevant features are the following:
It can generate good reports about the commonest QoS parameters like losses, one way delays etc, so it is a good tool not only to
be know the real QoS offered by the network but also to detect troubles on it.
As can be seen in figure below, the OpenIMP measurement system consists of N distributed Measurement Servers (impd), also known as
probes, a Result Data Collector (impcol), and the OpenIMP Shell (impsh) which can be used to send commands to the distributed
components and retrieve their return values.
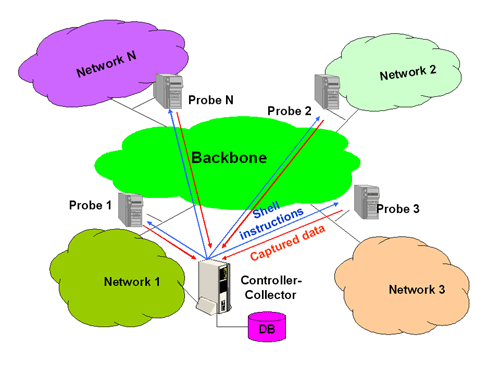
Components of the OpenIMP prototype
Alternatively to the shell, the OpenIMP offers a friendlier HTTP-based GUI, shown in next figure, to manage all the distributed
probes and to setup the measures that are going to be done. The usage of this interface is recommended.
The current OpenIMP release uses the 'scp' command to transfer the measurement result data from the Measurement Servers to the
Data Collector. On the Control PC (on which impd and impcol are located) a special user account is needed. This is used by the remote
measurement servers to scp the data. The authentication is done via public keys. In this way, confidentiality of the captured data by
the probes is provided.
The Measurement Controller PC hosts the Database, the WebServer used by the GUI, the Result Data Collector (impcol), a Measurement
Server (impd) started in QoS calculation mode for one-way delay measurements.
It is the part more complex to both install and manage since it consists of several pieces of software that are used by the
controller. Apache server, php modules, mysqlserver, gnuplot, rrdtool are only some of the required tools needed to get the
measurement controller working.
For this reason, we will only use one controller/collector hosted at Consulintel Laboratory to avoid the non-familiarized partners
to deal with those complex tasks. Hence, partners willing to participate on the QoS Measurement Deployment only need take care about
the installation of the probes.
On the other hand the measurement servers (probes) are in charge of capturing the IPv6 traffic going through the network where it
is attached and according to the configuration made by users through the GUI. The probe is the only component that the Euro6IX
partners willing to participate on the QoS Measurement Deployment need to install.
2.2. Recommended Platforms
The OpenIMP system can be installed in either a FreeBSD or Linux Operating System. It can work in any PC system, although features
like performance, packets lost while capturing, maximum flow bit rate, etc. can be highly influenced by the configuration of the
platform.
Hence, the minimum recommended platform configuration to achieve good results depends of the planned measured bit rates, according
to next table.
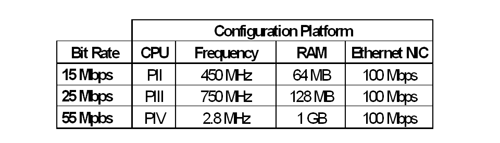
Recommended Platforms
Recommended Topology
In order to check the QoS deployment, the site recommended to install the probes is into the network of each partner deploying QoS
capabilities. Next figure shows two possible topologies.
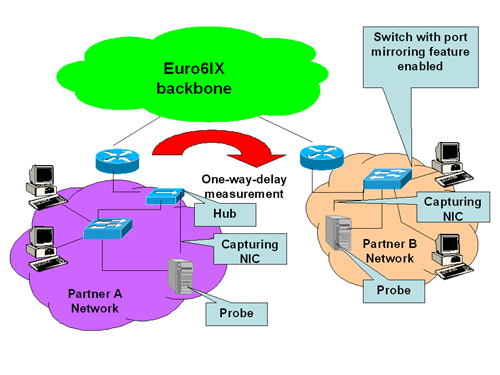
Recommended topologies
In partner A network it is shown a configuration where the probe uses a hub to sniff the same traffic that goes from/to the network.
The probe NIC for capturing traffic is attached to such a hub and the NIC for general purpose communication is attached to the switch
used for implementing the LAN segment.
In partner B network it is shown a configuration where only a switch is utilized. It is used for both implementing the LAN segment
and for allowing the probe to sniff the traffic. The switch has to have an Ethernet port enabled to do port mirroring, so all the
traffic going from/to the LAN segment is sent to such a port. The probe NIC used for capturing has to be attached to such a port.
The other NIC is attached to the switch as usual.
Both configurations are valid and every partner will decide which is better according to its infrastructure.
|







